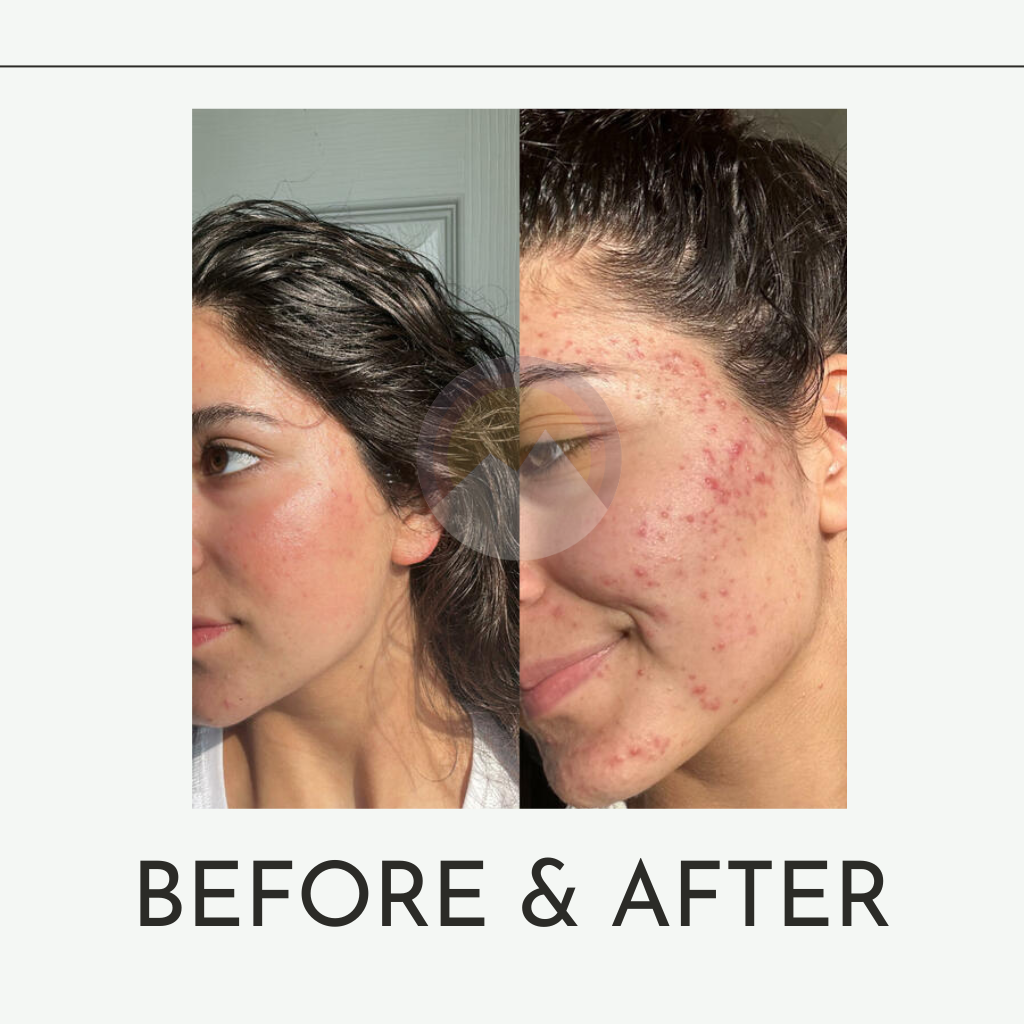
-
The artificial sweetener erythritol acutely affects gastrointestinal motility and microbiota in healthy humans: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36849732/ This study, published in Nature Medicine in 2023, found that consuming high doses of erythritol (compared to a control group) led to increased bloating and changes in gut bacteria in healthy individuals.
-
A Sugar Replacement May Be Linked to Heart Attacks and Strokes. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-023-02223-9 This Time Magazine article discusses the same study mentioned above, highlighting the potential link between high erythritol intake and cardiovascular events.
-
Modulation of gut microbiota by sugar alcohols: implications for health: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1521691803000349 (2020) - This review explores how different sugar alcohols, including erythritol, can influence gut microbiota composition. It highlights the potential for both beneficial and detrimental effects depending on the specific type and dosage of sugar alcohol consumed.
-
Impact of artificial sweeteners on gut bacteria growth: An in vitro study: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8156656/ (2018) - This in vitro study suggests that erythritol may inhibit the growth of some beneficial gut bacteria while promoting potentially harmful ones. However, in vitro studies don't always translate directly to human gut responses.
-
A review of the effects of sugar-free sweeteners on human health: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9261844/ (2016) - This review acknowledges that some studies suggest erythritol can alter gut bacteria composition, but highlights the need for more research to understand the long-term consequences of these changes and any potential health implications.
-
Prebiotics and synbiotics: Their role in gut microbiota modulation and related health benefits: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5622781/ (2019) - While not directly related to erythritol, this study provides valuable context on the importance of a healthy gut microbiome and the potential benefits of prebiotics for promoting its balance.
-
Non-nutritive sweeteners and metabolic health: a review: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6471792/ This 2017 review article discusses potential health concerns surrounding non-nutritive sweeteners, including erythritol. It mentions the possibility of gastrointestinal issues and the need for further research on long-term effects.
-
Effect of erythritol on gut microbiota and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) in healthy subjects: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S126236362100001X (2017) This study suggests erythritol may alter gut bacteria composition and potentially influence GLP-1, a hormone involved in blood sugar control.
-
Effect of different sugar alcohols on gastrointestinal motility and symptoms: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21576989/ (2017) This study compared various sugar alcohols, including erythritol, and found it may increase bloating and discomfort in some individuals.
-
Non-nutritive sweeteners and metabolic health: a review: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32521750/ (2017) This review highlights the need for further research on the long-term effects of non-nutritive sweeteners, including erythritol, on metabolism and blood sugar control.
-
The artificial sweetener erythritol acutely affects gastrointestinal motility and microbiota in healthy humans: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36849732/ (2023) While not a direct cause-and-effect study, this research suggests a possible link between high erythritol intake and changes in gut bacteria associated with increased cardiovascular risk.
-
Effect of erythritol on subjective satiety and hormonal responses in healthy subjects: https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/immunology-and-microbiology/satiety (2014) This study suggests erythritol may not be as effective as some other sweeteners in promoting feelings of fullness (satiety) after consumption. This could lead to increased calorie intake overall.
-
Sweet taste perception and energy intake: effects of steviol glycosides and erythritol in yogurt: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9824470/ (2013) This research explores how erythritol and stevia (often used together) might impact taste perception and energy intake in yogurt. The study suggests these sweeteners may not fully compensate for the reduced sweetness compared to sugar, potentially leading to people consuming larger portions to achieve the desired level of sweetness.
-
Erythritol: Safety and Kinetics: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36849732/ (2008) This review provides a general overview of erythritol, including its safety profile and how the body absorbs and eliminates it. It highlights the need for further research on long-term effects, particularly for high dose consumption.
Erythritol's Impact on Your Health